Liquid nitrogen expands 695 times in volume when it vaporizes and has no warning properties such as odor or color.
Liquid nitrogen tank venting.
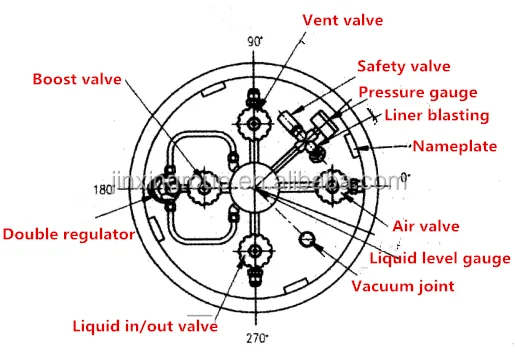
Ensure all safety valves and vent valves are unobstructed and functioning properly.
Check the safety vents on liquid nitrogen tanks at least twice a week.
Liquid withdrawal circuit this circuit takes liquid from the bot tom of the tank and deliv ers it directly to the liquid valve for customer use.
During transfer if pressure in the tank is higher than the normal liquid withdrawal pressure open the vent valve to lower the.
Transport the large low pressure liquid nitrogen cylinders used on campus are equipped with wheels and.
1990 specification for bursting discs and bursting disc devices british standards institution.
Safe handling and use of liquid nitrogen characteristics of nitrogen 78 of atmosphere colorless odorless tasteless and nontoxic boils at 320 degrees fahrenheit 196 c non flammable will not support life gas is slightly lighter than air liquid nitrogen facts 1 cubic foot of liquid nitrogen will expand to 696 cubic feet of 100 gaseous nitrogen at 70 f the nitrogen gas can displace the.
Then open the liquid use valve to allow head pressure in the tank head to force liquid up to withdrawal tube and out the liquid use valve.
Api std 2000 venting atmospheric and low pressure storage tanks.
Pressure may build up in liquid nitrogen storage cylinders.
Nonrefrigerated and refrigerated 1998.
Never pour cryogenic liquids into any drain.
In addition to these four circuits there is also a vent valve on the top of the tank that gives the end user or supplier the ability to vent the head pressure off of the tank for service or filling.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won t allow us.
Hence if sufficient liquid nitrogen is vaporized so as to reduce the oxygen percentage to below 19 5 there is a risk of oxygen deficiency which may cause unconsciousness.
Liquid withdrawal should be done at low pressure to prevent flash losses.
When ln2 boils it produces gaseous nitrogen which displaces oxygen from the air.
Hazards associated with liquid nitrogen asphyxiation.
Cold rooms are poorly ventilated small rooms and must not be used for the storage of liquid nitrogen vessels.
Use cryogenic liquids only in well ventilated areas or with local exhaust ventilation.